Poiseuille Pipe (Periodic)#
The simulation of a periodic Poiseuille pipe flow is used for the validation of the immersed boundary method (IBM) as to represent a curved boundary. In the current case, the external force density term represents the pressure gradient \(F_{x}=-\mathrm{d}p/\mathrm{d}x\), periodicity is considered in all boundaries, and an cylindrical Lagrangian mesh is placed with axis alligned to the \(x\)-axis.
from nassu.cfg.model import ConfigScheme
filename = "tests/validation/cases/03_poiseuille_pipe_flow.nassu.yaml"
sim_cfgs = ConfigScheme.sim_cfgs_from_file_dct(filename)
The simulation parameters are shown below
from nassu.cfg.schemes.simul import SimulationConfigs
import pandas as pd
dct = {"N": [], "F": [], "tau": [], "time_steps": []}
def add_to_dict(sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs):
dct["N"].append(sim_cfg.domain.domain_size.x)
dct["tau"].append(sim_cfg.models.LBM.tau)
dct["F"].append(sim_cfg.models.LBM.F.x)
dct["time_steps"].append(sim_cfg.n_steps)
sim_cfgs_use = [
sim_cfg
for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items()
if sim_cfg.name.startswith("periodicPoiseuillePipeN")
]
for sim_cfg in sim_cfgs_use:
add_to_dict(sim_cfg)
df = pd.DataFrame(dct, index=None)
df
| N | F | tau | time_steps | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24 | 6.250000e-05 | 0.8 | 2000 |
| 1 | 40 | 7.812500e-06 | 0.8 | 8000 |
| 2 | 72 | 9.765630e-07 | 0.8 | 32000 |
| 3 | 136 | 1.220700e-07 | 0.8 | 128000 |
Where N represents the domain size, directly correlated to the scale of the problem and the level of mesh refinement. Also, F is a volumetric force generating the flow. Since the domain size changes between cases F must be reescaled in order to keep the velocity profile constant.
An extra spacing of 2 lattices at each side of the cylinder is kept to assure a complete interpolation-spread procedure.
Functions to use for processing of poiseuille pipe.
from typing import Callable
import numpy as np
from lnas import LnasFormat
def get_poiseuille_pipe_analytical_func() -> Callable:
"""Poiseuille analytical velocity function
Returns:
Callable[[float], float]: Analytical velocity function
"""
return lambda r: 2 * (1 - r * r)
def get_poiseuille_pipe_numerical_avg_vel(ux_vals: np.ndarray) -> float:
# Average velocity is ~half the maximun velocity.
# Numerical integration gives worse results for average velocity
return np.max(ux_vals) / 2
def get_pos_values_inside_pipe(sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs) -> np.ndarray:
lnas_filename = sim_cfg.output.bodies["cylinder"].lnas_transformed
lnas = LnasFormat.from_file(lnas_filename)
vertices = lnas.geometry.vertices
x_val = sim_cfg.domain.domain_size.x / 2
z_val = sim_cfg.domain.domain_size.z / 2
min_y, max_y = (vertices[:, 1].min(), vertices[:, 1].max())
min_y, max_y = int(np.ceil(min_y)), int(np.ceil(max_y))
p1, p2 = (x_val, min_y, z_val), (x_val, max_y, z_val)
line = np.linspace(p1, p2, num=max_y - min_y, endpoint=False)
return line
def plot_analytical_poiseuille_pipe_vels(ax):
x = np.arange(
-1,
1.01,
0.01,
)
analytical_func = get_poiseuille_pipe_analytical_func()
analytical_data = analytical_func(x)
ax.plot(x, analytical_data, "--k", label="Analytical")
Results#
Extract the velocity profile from simulation
import numpy as np
from vtk.util.numpy_support import vtk_to_numpy
from tests.validation.notebooks import common
extracted_data = {}
array_to_extract = "ux"
for sim_cfg in sim_cfgs_use:
export_instantaneous_cfg = sim_cfg.output.instantaneous
macr_export = export_instantaneous_cfg["default"]
time_step = macr_export.time_steps(sim_cfg.n_steps)[-1]
reader = macr_export.read_vtm_export(time_step)
pos = get_pos_values_inside_pipe(sim_cfg)
# Sum 0.5 because data is cell data, so it's in the center of the cell
p1 = pos[0] + 0.5
p2 = pos[-1] + 0.5
line = common.create_line(p1, p2, len(pos) - 1)
# Get the points from the vtkLineSource
polyData = line.GetOutput()
points = polyData.GetPoints()
probe_filter = common.probe_over_line(line, reader.GetOutput())
probed_data = vtk_to_numpy(probe_filter.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetArray(array_to_extract))
extracted_data[(sim_cfg.sim_id, sim_cfg.name)] = {"pos": pos, "data": probed_data}
extracted_data.keys()
dict_keys([(0, 'periodicPoiseuillePipeN16'), (0, 'periodicPoiseuillePipeN32'), (0, 'periodicPoiseuillePipeN64'), (0, 'periodicPoiseuillePipeN128')])
The velocity profile at the end of simulation is compared with the steady state analytical solution below:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(6, 5)
style_num = ["o", "^", "s", "+", "x"]
def normalize_pos(pos):
# Normalize between -1 and 1
pos -= pos.min()
R = pos.max()
pos /= pos.max()
pos -= 0.5
pos *= 2
return R
for sim_cfg, mkr_style in zip(sim_cfgs_use, style_num):
num_data = extracted_data[(sim_cfg.sim_id, sim_cfg.name)]
num_avg_vel = get_poiseuille_pipe_numerical_avg_vel(num_data["data"])
pos_norm = num_data["pos"][:, 1].copy()
R = normalize_pos(pos_norm)
ax.plot(
pos_norm,
num_data["data"] / num_avg_vel,
mkr_style,
label=f"R={R} (avg. {num_avg_vel:.2e})",
fillstyle="none",
c="k",
)
sim_cfg_ref = sim_cfgs_use[0]
plot_analytical_poiseuille_pipe_vels(ax)
ax.set_title(
f"Poiseuille (Periodic)\n({sim_cfg_ref.models.LBM.vel_set} {sim_cfg_ref.models.LBM.coll_oper})"
)
ax.legend()
plt.show(fig)
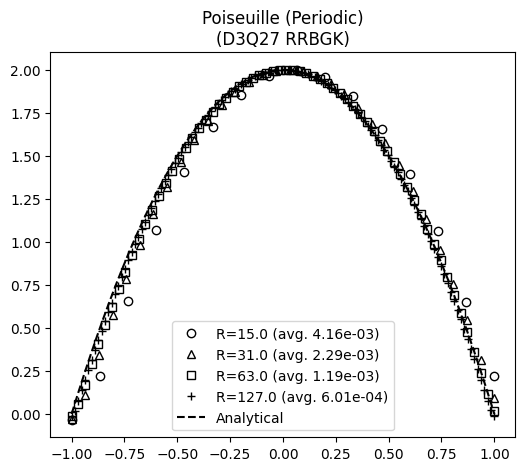
The first order error decay under grid refinement for the present case is also verified:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(6, 5)
analytical_error_prof: list[float] = []
numerical_error_prof: list[float] = []
N_list: list[int] = []
analytical_func = get_poiseuille_pipe_analytical_func()
for sim_cfg in sim_cfgs_use:
num_data = extracted_data[(sim_cfg.sim_id, sim_cfg.name)]
num_avg_vel = get_poiseuille_pipe_numerical_avg_vel(num_data["data"])
num_pos = num_data["pos"][:, 1].copy()
R = num_pos.max() - num_pos.min()
normalize_pos(num_pos)
num_profile = num_data["data"] / num_avg_vel
num_o2_error = common.get_o2_error(num_pos, num_profile, analytical_func)
analyical_error = (
num_o2_error if len(analytical_error_prof) == 0 else analytical_error_prof[-1] / 4
)
analytical_error_prof.append(analyical_error)
numerical_error_prof.append(num_o2_error)
N_list.append(R)
ax.plot(N_list, numerical_error_prof, "sk", fillstyle="none", label="Numerical")
ax.plot(N_list, analytical_error_prof, "--k", label=r"$O(\Delta x^2)$")
ax.set_yscale("log")
ax.set_xscale("log", base=2)
ax.set_title(
r"Poiseuille $O(\Delta x^2)$ (Periodic)"
+ f"\n({sim_cfg.models.LBM.vel_set} {sim_cfg.models.LBM.coll_oper})"
)
ax.legend()
plt.show(fig)
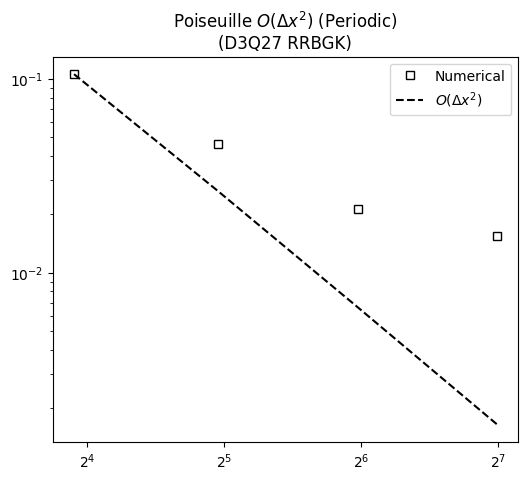
The results show that the flow evolution equation from LBM converges to steady analytical solution.
Version#
sim_info = sim_cfg.output.read_info()
nassu_commit = sim_info["commit"]
nassu_version = sim_info["version"]
print("Version:", nassu_version)
print("Commit hash:", nassu_commit)
Version: 1.6.33
Commit hash: fbc0edb5260d2734f0a290e1806c26ac6d865ff4
Configuration#
from IPython.display import Code
Code(filename=filename)
simulations:
- name: periodicPoiseuillePipeN16
save_path: ./tests/validation/results/03_poiseuille_pipe_flow/periodic
n_steps: 2000
report:
frequency: 1000
data:
divergence: { frequency: 50 }
instantaneous:
default: { interval: { frequency: 0 }, macrs: [rho, u, f_IBM, S] }
domain:
domain_size:
x: 24
y: 24
z: 24
block_size: 8
bodies:
cylinder:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/cylinder.lnas
small_triangles: add
transformation:
scale: [8, 8, 8]
translation: [-4, 4, 4]
models:
precision:
default: single
LBM:
tau: 0.8
F:
x: 6.25E-05
y: 0
z: 0
vel_set: D3Q27
coll_oper: RRBGK
engine:
name: CUDA
IBM:
forces_accomodate_time: 1000
body_cfgs:
default: {}
BC:
periodic_dims: [true, false, false]
BC_map:
- pos: N
BC: RegularizedHWBB
wall_normal: N
order: 1
- pos: S
BC: RegularizedHWBB
wall_normal: S
order: 1
- pos: F
BC: RegularizedHWBB
wall_normal: F
order: 2
- pos: B
BC: RegularizedHWBB
wall_normal: B
order: 2
- name: periodicPoiseuillePipeN32
parent: periodicPoiseuillePipeN16
n_steps: 8000
domain:
domain_size:
x: 40
y: 40
z: 40
block_size: 8
bodies: !not-inherit
cylinder:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/cylinder.lnas
small_triangles: add
transformation:
scale: [16, 16, 16]
translation: [-4, 4, 4]
models:
LBM:
F:
x: 7.8125E-06
y: 0
z: 0
- name: periodicPoiseuillePipeN64
parent: periodicPoiseuillePipeN16
n_steps: 32000
domain:
domain_size:
x: 72
y: 72
z: 72
block_size: 8
bodies: !not-inherit
cylinder:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/cylinder.lnas
small_triangles: add
transformation:
scale: [32, 32, 32]
translation: [-4, 4, 4]
models:
LBM:
F:
x: 9.76563E-07
y: 0
z: 0
- name: periodicPoiseuillePipeN128
parent: periodicPoiseuillePipeN16
n_steps: 128000
domain:
domain_size:
x: 136
y: 136
z: 136
block_size: 8
bodies: !not-inherit
cylinder:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/cylinder.lnas
small_triangles: add
transformation:
scale: [64, 64, 64]
translation: [-4, 4, 4]
models:
LBM:
F:
x: 1.22070E-07
y: 0
z: 0
- name: velocityNeumannPoiseuillePipeMultilevel
save_path: ./tests/validation/results/03_poiseuille_pipe_flow/velocity_neumann_multilevel
n_steps: 32000
report:
frequency: 1000
data:
divergence: { frequency: 1 }
instantaneous:
default: { interval: { frequency: 8000 }, macrs: [rho, u, f_IBM, S] }
domain:
domain_size:
x: 104
y: 32
z: 32
block_size: 8
bodies_domain_limits:
start: [4, 8, 8]
end: [88, 40, 40]
is_abs: true
bodies:
cylinder:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/cylinder.lnas
small_triangles: add
transformation:
scale: [8, 8, 8]
translation: [4, 8, 8]
refinement:
static:
default:
bodies:
- body_name: cylinder
lvl: 1
normal_offsets: [-2, 0, 2]
models:
precision:
default: single
LBM:
tau: 0.51
vel_set: D3Q27
coll_oper: RRBGK
engine:
name: CUDA
BC:
periodic_dims: [false, false, false]
BC_map:
- pos: W
BC: UniformFlow
wall_normal: W
rho: 1.0
ux: 0.05
uy: 0
uz: 0
order: 2
- pos: E
BC: RegularizedNeumannOutlet
rho: 1.0
wall_normal: E
order: 2
- pos: N
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: N
order: 1
- pos: S
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: S
order: 1
- pos: F
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: F
order: 0
- pos: B
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: B
order: 0
IBM:
forces_accomodate_time: 1000
body_cfgs:
default: {}
