Turbulent Channel (Reynolds 2003)#
The simulation of a periodic turbulent channel is also used for validation of the equilibrium wall model implemented with the thin boundary layer (TBL) equation. A friction Reynolds number of 2003 is fixed for this case. The reference article used for comparison of results is Han et al., 2020. The pressure gradient is estabilished through a constant body force.
from nassu.cfg.model import ConfigScheme
filename = "tests/validation/cases/04.1_turbulent_channel_flow_wm.nassu.yaml"
sim_cfgs = ConfigScheme.sim_cfgs_from_file_dct(filename)
sim_cfg = next(
sim_cfg
for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items()
if sim_cfg.name == "periodicTurbulentChannel"
)
sim_cfg_wm = next(
sim_cfg
for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items()
if sim_cfg.name == "periodicTurbulentChannelMultilevel"
)
sim_cfg_wm_mb = next(
sim_cfg
for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items()
if sim_cfg.name == "periodicTurbulentChannelNoWM"
)
sim_cfgs_use = {"ref": sim_cfg, "wm": sim_cfg_wm, "mb": sim_cfg_wm_mb}
Functions to use for turbulence channel processing
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pathlib
from nassu.cfg.schemes.simul import SimulationConfigs
from vtk.util.numpy_support import vtk_to_numpy
from tests.validation.notebooks import common
def get_experimental_profiles(reynolds_tau: float) -> dict[str, pd.DataFrame]:
files_tau: dict[float, dict[str, str]] = {
2003: {
"ux": "Turbulent_channel/Re_tau_2003/u_avg.csv",
"ux_rms": "Turbulent_channel/Re_tau_2003/u_rms.csv",
"uy_rms": "Turbulent_channel/Re_tau_2003/v_rms.csv",
"uz_rms": "Turbulent_channel/Re_tau_2003/w_rms.csv",
},
}
files_get = files_tau[reynolds_tau]
vals_exp: dict[str, pd.DataFrame] = {}
for name, comp_file in files_get.items():
filename = pathlib.Path("tests/validation/comparison") / comp_file
df = pd.read_csv(filename, delimiter=",")
vals_exp[name] = df
return vals_exp
def get_height_scale(sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs, reynolds_tau: float, u_ref: float) -> float:
kin_visc = sim_cfg.models.LBM.kinematic_viscosity
return u_ref / kin_visc
reader_output = {}
for name, sim_cfg in sim_cfgs_use.items():
stats_export = sim_cfg.output.stats["default"]
last_step = stats_export.interval.get_all_process_steps(sim_cfg.n_steps)[-1]
reader = stats_export.read_vtm_export(last_step)
reader_output[sim_cfg.name] = reader.GetOutput()
def get_macr_compressed(
sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs, macr_name: str, is_2nd_order: bool
) -> np.ndarray:
global reader, reader_output
output_use = reader_output[sim_cfg.name]
macr_name_read = macr_name if not is_2nd_order else f"{macr_name}_2nd"
ds = sim_cfg.domain.domain_size
p0 = np.array((ds.x // 2, ds.y // 2, 4))
p1 = np.array((ds.x // 2, ds.y // 2, ds.z // 2))
n_points = ds.z - 8
pos = np.linspace(p0, p1, num=n_points, endpoint=True)
norm_pos = (pos[:, 2] - 4) / (ds.z - 8)
# Sum 0.5 because data is cell centered in vtm
line = common.create_line(p0, p1, n_points - 1)
probe_filter = common.probe_over_line(line, output_use)
probed_data = vtk_to_numpy(probe_filter.GetOutput().GetPointData().GetArray(macr_name_read))
return np.array([norm_pos, probed_data])
y, ux_avg = get_macr_compressed(sim_cfg, "ux", is_2nd_order=False)
Results#
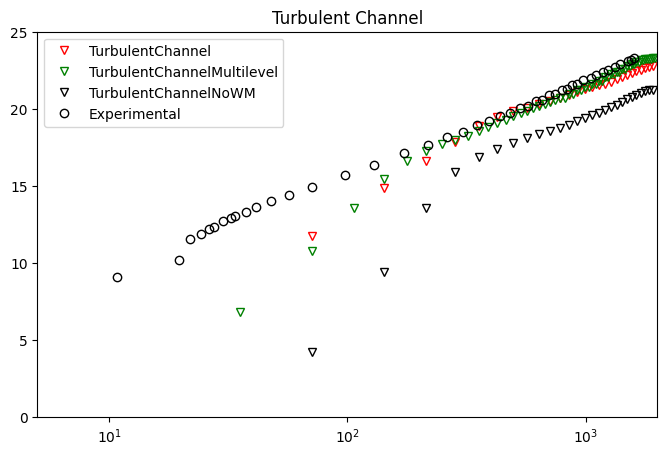
The average velocity profile is shown for the case. It can be seen a good approximation of desired profile when using the wall model.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
reynolds_tau = 2003
u_ref = 0.00225
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
fig.set_size_inches(8, 5)
for i, (sim_cfg, color) in enumerate(zip(sim_cfgs_use.values(), ("r", "g", "k"))):
height_scale = get_height_scale(sim_cfg, reynolds_tau, u_ref)
name = sim_cfg.name.removeprefix("periodic")
analytical_values = get_experimental_profiles(reynolds_tau)
y, ux_avg = get_macr_compressed(sim_cfg, "ux", is_2nd_order=False)
if not sim_cfg.name.endswith("Multilevel"):
y, ux_avg = y[::2], ux_avg[::2]
ux_avg /= u_ref
y *= height_scale * (sim_cfg.domain.domain_size.z - 8)
exp_y = analytical_values["ux"]["y+"]
exp_ux_avg = analytical_values["ux"]["u/u*"]
ax.plot(y, ux_avg, f"v{color}", label=f"{name}", fillstyle="none")
ax.plot(exp_y, exp_ux_avg, "ok", label="Experimental", fillstyle="none")
ax.set_title("Turbulent Channel")
ax.legend(loc="upper left")
ax.set_xlim(5, 2000)
ax.set_ylim(0, 25)
ax.set_xscale("symlog")
The results of the \({\mathrm{u_{rms}}}\) velocity profiles shown below also indicate a good representation with the multilevel approach.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3)
fig.set_size_inches(20, 5)
vel_name_map = {"ux": "u", "uy": "v", "uz": "w"}
for i, sim_cfg in enumerate(sim_cfgs_use.values()):
name = sim_cfg.name.removeprefix("periodic")
for macr_name, marker, color in [("ux", "o", "k"), ("uy", "^", "r"), ("uz", "s", "b")]:
macr_compr_rms = get_macr_compressed(sim_cfg, macr_name, is_2nd_order=True)
macr_compr_avg = get_macr_compressed(sim_cfg, macr_name, is_2nd_order=False)
y = macr_compr_rms[0].copy()
vel_2nd = macr_compr_rms[1].copy()
vel_avg = macr_compr_avg[1].copy()
vel_rms = (vel_2nd - vel_avg**2) ** 0.5
vel_rms /= u_ref
y *= height_scale * (sim_cfg.domain.domain_size.z - 8)
# Remove wall value
vel_rms = vel_rms[::2]
y = y[::2]
name_vel = vel_name_map[macr_name]
df = analytical_values[f"{macr_name}_rms"]
exp_y = df["y+"]
exp_rms = df[f"{name_vel}'/u*"]
ax[i].plot(y, vel_rms, f"v{color}", label=f"{name} {name_vel.upper()}")
ax[i].plot(
exp_y, exp_rms, f"{marker}{color}", label=f"Exp. {name_vel.upper()}", fillstyle="none"
)
# ax[i].set_xscale("symlog")
ax[i].set_title(f"{name}")
ax[i].legend()
ax[i].set_xlim(10, 2000)
ax[i].set_ylim(0, 3.5)
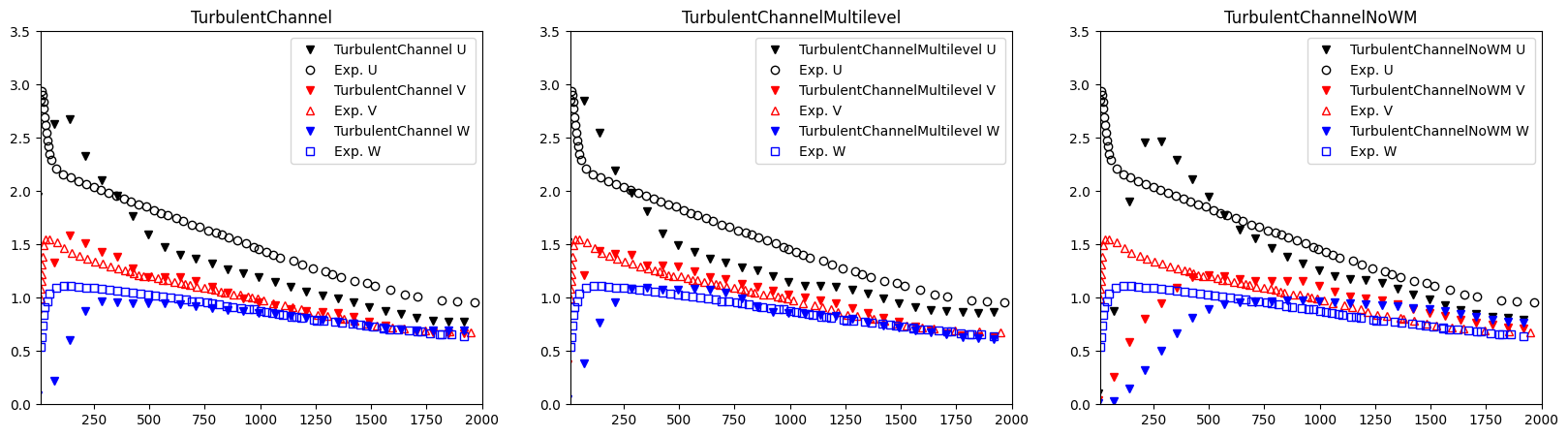
It can be seen good approach of results with the use of wall model and subsequent combination with multigrid approach. As the shell point becomes nearer the surface for a high refinement, the first point velocity becomes a little smaller than for a coarser refinement.
Version#
sim_info = sim_cfg.output.read_info()
nassu_commit = sim_info["commit"]
nassu_version = sim_info["version"]
print("Version:", nassu_version)
print("Commit hash:", nassu_commit)
Version: 1.6.40
Commit hash: 79342cd137bdb267e91047977e942600a6962053
Configuration#
from IPython.display import Code
Code(filename=filename)
simulations:
- name: periodicTurbulentChannel
save_path: ./tests/validation/results/04.1_turbulent_channel_flow_wm/periodic
run_simul: true
n_steps: 200000
report:
frequency: 1000
domain:
domain_size:
x: 168
y: 168
z: 64 # spacing 56
block_size: 8
bodies:
plane_floor:
IBM:
run: True
cfg_use: plane_cfg
order: 0
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/wind_tunnel/full_plane.lnas
transformation:
scale: [2, 2, 2]
translation: [0, 0, 4]
plane_ceil:
IBM:
run: True
cfg_use: plane_cfg
order: 0
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/wind_tunnel/full_plane.lnas
transformation:
scale: [2, 2, 2]
fixed_point: [0, 80, 0]
rotation: !math [radians(180), 0, 0]
translation: [0, 0, 60]
data:
export_IBM_nodes:
ibm_exp:
body_name: plane_floor
frequency: 5000
divergence: { frequency: 1 }
instantaneous:
default: { interval: { frequency: 5000 }, macrs: [rho, u, omega_LES, f_IBM] }
statistics:
interval: { frequency: 100, start_step: 100000 }
macrs_1st_order: [rho, u]
macrs_2nd_order: [u]
exports:
default: { interval: { frequency: 50000 } }
models:
precision:
default: single
LBM:
tau: 0.500096682620786
F:
x: 1.89820067659664E-07
y: 0
z: 0
vel_set: D3Q27
coll_oper: RRBGK
initialization:
vtm_filename: "../nassuArtifacts/macrs/turbulent_channel_wm.vtm"
engine:
name: CUDA
LES:
model: Smagorinsky
sgs_cte: 0.17
BC:
periodic_dims: [true, true, true]
IBM:
dirac_delta: 3_points
forces_accomodate_time: 0
reset_forces: true
body_cfgs:
default:
n_iterations: 1
forces_factor: 1.0
plane_cfg:
n_iterations: 1
forces_factor: 0.25
wall_model:
name: EqTBL
dist_ref: 2.0
dist_shell: 0.25
start_step: 0
params:
z0: 0.00155
TDMA_max_error: 1e-04
TDMA_max_iters: 10
TDMA_min_div: 51
TDMA_max_div: 51
visc_correction: False
multiblock:
overlap_F2C: 2
- name: periodicTurbulentChannelMultilevel
parent: periodicTurbulentChannel
run_simul: true
domain:
refinement:
static:
default:
volumes_refine:
- start: [0, 0, 0]
end: [168, 168, 16]
lvl: 1
is_abs: true
- start: [0, 0, 48]
end: [168, 168, 64]
lvl: 1
is_abs: true
- name: periodicTurbulentChannelNoWM
parent: periodicTurbulentChannel
run_simul: true
models:
IBM:
body_cfgs:
plane_cfg:
wall_model: null
