Flow Over Stationary Sphere#
The simulation of a laminar flow over a stationary sphere is used for the validation of force spreading aspects of the immersed boundary method (IBM). For that purpose, the drag coefficient is measured through the forces calculated at the Lagrangian mesh.
from nassu.cfg.model import ConfigScheme
filename = "tests/validation/cases/07_flow_over_sphere.nassu.yaml"
sim_cfgs = ConfigScheme.sim_cfgs_from_file_dct(filename)
A multilevel configuration is adopted to allow a large ratio between the sphere’s and domain’s sizes.
sim_laminar = [sim_cfg for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items() if name.startswith("laminar")]
sim_turb = next(
sim_cfg for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items() if name == "turbulentFlowOverSphere"
)
sim_turb_les = next(sim_cfg for (name, _), sim_cfg in sim_cfgs.items() if name.endswith("LES"))
sim_cfgs_use = sim_laminar + [sim_turb] + [sim_turb_les]
Functions to use for flow over sphere processing
import pandas as pd
import pathlib
from nassu.cfg.schemes.simul import SimulationConfigs
def get_experimental_profile_Cp(reynolds: float) -> pd.DataFrame:
files_tau: dict[float, str] = {
4200: "Flow_over_sphere/Re_4200/Cp_vs_theta.csv",
50000: "Flow_over_sphere/Re_50000/Cp_vs_theta.csv",
300000: "Flow_over_sphere/Re_300000/Cp_vs_theta.csv",
400000: "Flow_over_sphere/Re_400000/Cp_vs_theta.csv",
1140000: "Flow_over_sphere/Re_1140000/Cp_vs_theta.csv",
}
file_get = files_tau[reynolds]
filename = pathlib.Path("tests/validation/comparison") / file_get
# ([theta], [Cp])
df = pd.read_csv(filename, delimiter=",")
return df
def get_experimental_profile_Cd() -> pd.DataFrame:
file_get = "Flow_over_sphere/drag_coefficient.csv"
filename = pathlib.Path("tests/validation/comparison") / file_get
# ([Author], [Re], [Cd])
df = pd.read_csv(filename, delimiter=",")
return df
u_reference = 0.00549
def get_height_scale(sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs, reynolds: float) -> float:
global u_reference
kin_visc = sim_cfg.models.LBM.kinematic_viscosity
return u_reference / kin_visc
Results#
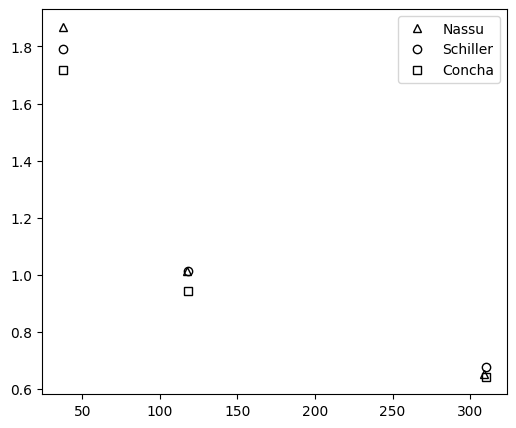
Good agreement with correlations found in literature is found for the drag coefficient, with better results achieved at higher Reynolds number. For such cases, the boundary proximity is expected to have smaller effect in the result of drag coefficient.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(6, 5)
num_vals = {"x": [], "y": []}
for sim_cfg in sim_laminar:
output_sphere = sim_cfg.output.bodies["sphere"]
last_step = output_sphere.interval.get_all_process_steps(sim_cfg.n_steps)[-1]
filename_nodes = output_sphere.nodes_data_csv(last_step)
df_body = pd.read_csv(filename_nodes)
diameter = df_body["pos_x"].max() - df_body["pos_x"].min()
# Force in flow direction
sum_F = df_body["force_x"].sum()
# Average rho
rho_inf = 1
# Inlet velocity
u_inf = max(bc.ux for bc in sim_cfg.models.BC.BC_map if "ux" in bc.model_dump())
# Circunference area
sphere_lvl = df_body["lvl"].max()
area = np.pi * (diameter * 2**sphere_lvl) ** 2 / 4
reynolds = u_inf * diameter / sim_cfg.models.LBM.kinematic_viscosity
Cd = -sum_F / (0.5 * rho_inf * area * u_inf**2)
num_vals["x"].append(reynolds)
num_vals["y"].append(Cd)
ax.plot(num_vals["x"], num_vals["y"], "^k", fillstyle="none", label="Nassu")
df_exp = get_experimental_profile_Cd()
authors = ["Schiller", "Concha"]
styles = ["ok", "sk"]
for author, style in zip(authors, styles):
ax.plot(df_exp["Re"], df_exp[author], style, fillstyle="none", label=author)
ax.legend()
plt.show(fig)
The pressure coefficient for the case of turbulent flow around a stationary sphere is performed for a Re=4,200 simulation to check capacity of measuring the pressure coefficient using the historic series function for a body. A posterior LES simulation is then performed for a Re=50,000 to also verify the solver stability for high Reynolds simulations. In both cases, excellent agreement with experimental data was obtained.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.set_size_inches(12, 5)
def post_proc_crossflow_sphere_Cp(
sim_cfg: SimulationConfigs, ax, reynolds: float, u_inf: float = 0.05
):
hs = sim_cfg.output.series["default"].bodies["sphere"]
df_points = pd.read_csv(hs.points_filename)
df_hs = hs.read_full_data("rho")
sphere_center = tuple(df_points[d].mean() for d in ("x", "y", "z"))
# Use only points in z=0 to calculate Cp
bool_arr = np.zeros((len(df_points),), dtype=np.bool_)
df_points = df_points.loc[
(df_points["z"] <= sphere_center[2] + 0.5) & (df_points["z"] >= sphere_center[2] - 0.5)
]
bool_arr[df_points["idx"]] = True
# TODO: This comes from sim_cfg, now hand written,
# but update to calculate it automatically
rho_inf = 1
df_hs = df_hs[df_hs["time_step"] >= 10000]
df_rho = df_hs.drop(columns="time_step")
df_cp = (df_rho - rho_inf) / (1.5 * rho_inf * (u_inf**2))
Cp_avg = df_cp.mean().to_numpy().T
Cp_avg = Cp_avg[bool_arr]
# Get angles for points, use acos because it goes from 0 to 180
x = df_points["x"] - df_points.mean()["x"]
y = df_points["y"] - df_points.mean()["y"]
points_angles: np.ndarray = np.arccos(-x / (x**2 + y**2) ** 0.5)
# Convert to angles
points_angles *= 180 / np.pi
points_angles = np.array(points_angles)
# # Sort arrays
argsort = points_angles.argsort()
points_angles = points_angles[argsort]
cp_points = Cp_avg[argsort]
ax.plot(points_angles, cp_points, "--k", label="Nassu")
df_exp = get_experimental_profile_Cp(reynolds)
ax.plot(df_exp["theta"], df_exp["Cp"], "ok", label="Experimental")
ax.legend()
for i, (sim_cfg, reynolds) in enumerate([(sim_turb, 4200), (sim_turb_les, 50000)]):
post_proc_crossflow_sphere_Cp(sim_cfg, ax[i], reynolds, u_inf=0.05)
ax[i].set_xlim((0, 180))
ax[i].set_ylim((-0.6, 1.2))
ax[i].set_ylabel("$C_p$")
ax[i].set_xlabel(r"$\theta$ (º)")
ax[i].grid()
ax[i].set_title(f"$Re={reynolds}$")
plt.show(fig)
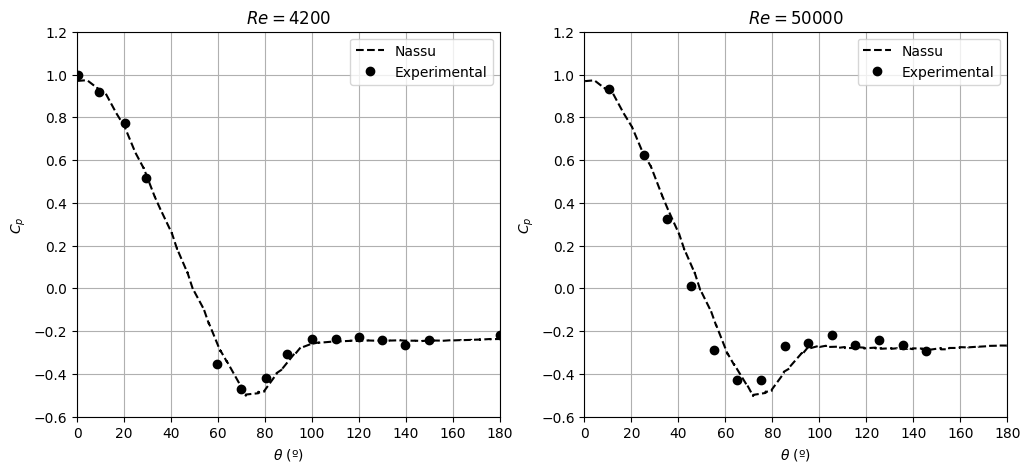
The pressure coefficient curve is very similar for both Re = 4200 and Re= 50,000. It can be seen better proximity of results in the LES simulation with a higher Reynolds number.
Version#
sim_info = sim_cfg.output.read_info()
nassu_commit = sim_info["commit"]
nassu_version = sim_info["version"]
print("Version:", nassu_version)
print("Commit hash:", nassu_commit)
Version: 1.6.33
Commit hash: fbc0edb5260d2734f0a290e1806c26ac6d865ff4
Configuration#
from IPython.display import Code
Code(filename=filename)
simulations:
- name: laminarFlowOverSphere
save_path: ./tests/validation/results/07_flow_over_sphere/laminar
n_steps: 40000
report: { frequency: 1000 }
domain:
domain_size:
x: 480
y: 160
z: 160
block_size: 8
bodies:
sphere:
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/sphere.lnas
transformation:
scale: [1.6, 1.6, 1.6]
translation: [112, 72, 72]
refinement:
static:
default:
volumes_refine:
- start: [96, 64, 64]
end: [160, 96, 96]
lvl: 1
is_abs: true
data:
divergence: { frequency: 10 }
instantaneous:
default: { interval: { frequency: 1000 }, macrs: [rho, u] }
export_IBM_nodes:
frequency: 5000
models:
precision:
default: single
LBM:
tau: 0.51
vel_set: D3Q27
coll_oper: RRBGK
initialization:
rho: 1.0
u:
x: !unroll [0.007854, 0.024583, 0.064583]
y: 0
z: 0
engine:
name: CUDA
BC:
periodic_dims: [false, false, false]
BC_map:
- pos: N
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: N
order: 0
- pos: S
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: S
order: 0
- pos: F
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: F
order: 1
- pos: B
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: B
order: 1
- pos: E
BC: RegularizedNeumannOutlet
rho: 1.0
wall_normal: E
order: 2
- pos: W
BC: UniformFlow
wall_normal: W
rho: 1
ux: !unroll [0.007854, 0.024583, 0.064583]
uy: 0
uz: 0
order: 2
- pos: NF
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: N
order: 0
- pos: NB
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: N
order: 0
- pos: SF
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: S
order: 0
- pos: SB
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: S
order: 0
- pos: NF
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: F
order: 1
- pos: NB
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: B
order: 1
- pos: SF
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: F
order: 1
- pos: SB
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: B
order: 1
IBM:
forces_accomodate_time: 1000
body_cfgs:
default: {}
multiblock:
overlap_F2C: 2
- name: turbulentFlowOverSphere
parent: laminarFlowOverSphere
save_path: ./tests/validation/results/07_flow_over_sphere/turbulent
n_steps: 100000
domain:
domain_size:
x: 640
y: 128
z: 128
block_size: 8
bodies: !not-inherit
sphere:
small_triangles: "add"
lnas_path: fixture/lnas/basic/sphere.lnas
transformation:
scale: [0.8, 0.8, 0.8]
translation: [112, 60, 60]
refinement:
static:
default:
volumes_refine:
- start: [96, 32, 32]
end: [224, 96, 96]
lvl: 1
is_abs: true
- start: [104, 56, 56]
end: [144, 72, 72]
lvl: 3
is_abs: true
data:
probes:
historic_series:
default:
macrs: ["u", "rho"]
interval: { frequency: 20, lvl: 0 }
bodies:
sphere:
body_name: sphere
normal_offset: 0.25
models:
LBM:
tau: 0.500285714285714
vel_set: D3Q27
coll_oper: RRBGK
initialization: !not-inherit
rho: 1.0
u:
x: 0.05
y: 0
z: 0
IBM:
forces_accomodate_time: 5000
multiblock:
overlap_F2C: 2
BC:
periodic_dims: [false, false, false]
BC_map:
- pos: N
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: N
order: 0
- pos: S
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: S
order: 0
- pos: F
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: F
order: 1
- pos: B
BC: Neumann
wall_normal: B
order: 1
- pos: E
BC: RegularizedNeumannOutlet
rho: 1.0
wall_normal: E
order: 2
- pos: W
BC: UniformFlow
wall_normal: W
rho: 1
ux: 0.05
uy: 0
uz: 0
order: 2
- name: turbulentFlowOverSphereLES
parent: turbulentFlowOverSphere
models:
LBM:
tau: 0.500024
LES:
model: Smagorinsky
sgs_cte: 0.17
